1. Introduction to EPS
What is EPS?
Earnings Per Share (EPS) is a financial metric that measures the profitability of a company. It represents the portion of a company’s earnings allocated to each outstanding share of common stock. EPS provides valuable insights into a company’s ability to generate profits and distribute them to shareholders.
How is EPS calculated?
EPS is calculated by dividing the net earnings of a company by the number of outstanding shares. The formula for calculating EPS is as follows:
EPS = Net Earnings / Number of Outstanding Shares
Net earnings can be derived from the company’s income statement, while the number of outstanding shares is typically disclosed in the company’s financial statements or annual reports.
2. Importance of EPS in Stock Investing
EPS is a fundamental metric used by investors to evaluate the financial performance of a company. Here are some key reasons why EPS is important in stock investing:
Assessing profitability
EPS provides a clear measure of a company’s profitability on a per-share basis. By analyzing EPS trends over time, investors can assess whether a company is consistently generating profits and increasing shareholder value.
Comparing companies within an industry
EPS allows investors to compare the financial performance of different companies within the same industry. This helps in identifying companies that are outperforming their peers and may have a competitive advantage.
Analyzing historical EPS trends
By analyzing historical EPS trends, investors can gain insights into a company’s earnings stability and growth potential. Consistently increasing EPS over time is often viewed as a positive sign, indicating a company’s ability to generate sustainable profits.
Evaluating growth potential
EPS growth is a key indicator of a company’s future prospects. Companies with high EPS growth rates are often considered attractive investments, as they demonstrate the potential for increased profitability and stock price appreciation.
3. Understanding PE Ratio
Definition of PE Ratio
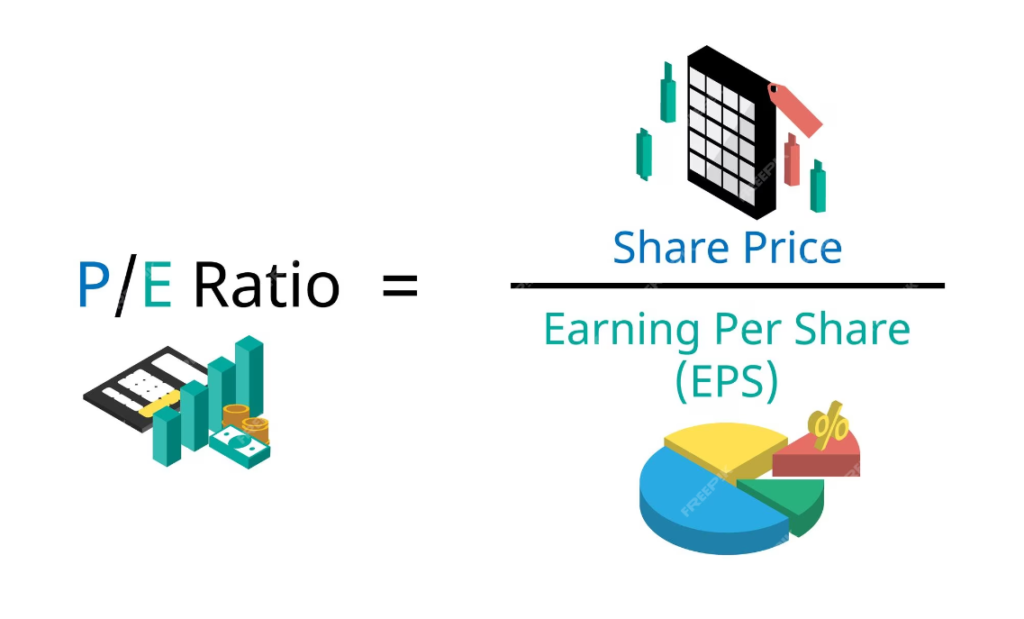
The Price-to-Earnings (PE) Ratio is a valuation metric that compares a company’s stock price with its earnings per share (EPS). It provides insights into how much investors are willing to pay for each unit of earnings generated by the company.
Calculation of PE Ratio
PE Ratio is calculated by dividing the stock price by the EPS. The formula for calculating PE Ratio is as follows:
PE Ratio = Stock Price / EPS
For example, if a stock is trading at ₹50 and its EPS is ₹10, the PE Ratio would be 50/10=5. The PE Ratio indicates the number of times investors are willing to pay for the company’s earnings.
4. Types of PE Ratios
Trailing PE Ratio
Trailing PE Ratio is calculated using the historical EPS of a company over the last 12 months. It provides a snapshot of a company’s valuation based on its most recent earnings performance.
Forward PE Ratio
Forward PE Ratio is calculated using the estimated future earnings of a company. Analysts use earnings forecasts to determine the expected growth rate of a company and assess its valuation based on future earnings potential.
5. Interpreting PE Ratio
Evaluating valuation
PE Ratio is a key indicator of a company’s valuation. A high PE Ratio suggests that investors are willing to pay a premium for the company’s earnings, indicating an expectation of future growth. Conversely, a low PE Ratio may indicate undervaluation, presenting an opportunity for potential value investors.
Comparing PE ratios within an industry
To gain a better understanding of a company’s valuation, it is essential to compare its PE Ratio with those of its industry peers. This comparison helps identify companies that may be overvalued or undervalued relative to their competitors.
Considering historical averages
Evaluating a company’s PE Ratio in the context of its historical averages provides insights into its valuation trend. Comparing the current PE Ratio with the company’s historical range can help determine whether the stock is trading at a premium or a discount.
6. Growth vs. Value Stocks
High PE ratio and growth stocks
A high PE Ratio is often associated with growth stocks. These stocks tend to have higher valuations because investors have high expectations for their future earnings growth. However, high PE Ratios also carry the risk of a potential market correction if the expected growth does not materialize.
Low PE ratio and value stocks
A low PE Ratio is typically associated with value stocks. These stocks are considered undervalued relative to their earnings and may present an opportunity for investors seeking bargains. Value stocks often have lower PE Ratios due to perceived risks or market pessimism.
7. Limitations of EPS and PE Ratio
Ignoring EPS growth rate
While EPS and PE Ratio provide valuable insights into a company’s financial performance and valuation, they do not consider the EPS growth rate. It is essential to analyze the growth potential of a company’s earnings to make a more informed investment decision.
Fluctuation of stock prices
PE Ratio is influenced by stock prices, which can fluctuate daily. As a result, the PE Ratio may not accurately reflect a company’s true value over an extended period. It is crucial to consider other factors and perform a thorough analysis before making investment decisions solely based on PE Ratio.
Considering other factors for investment decisions
EPS and PE Ratio should be used in conjunction with other financial metrics and qualitative factors to make well-informed investment decisions. Factors such as cash flow, industry trends, management quality, and competitive advantages should also be considered to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s investment potential.
8. Practical Application of EPS and PE Ratio
Industry-specific analysis
When analyzing companies within a specific industry, EPS and PE Ratio provide a basis for comparison. By comparing the EPS and PE Ratio of different companies within the same industry, investors can identify companies with stronger financial performance and relative valuation advantages.
Peer comparison
Comparing a company’s EPS and PE Ratio with its industry peers allows investors to assess its competitive position. Companies with higher EPS and lower PE Ratios compared to their peers may indicate superior financial performance and valuation attractiveness.
Future earnings estimation
Forward PE Ratio is particularly useful for assessing a company’s future earnings potential. By considering estimated future earnings, investors can gauge the growth prospects of a company and make informed investment decisions.
9. EPS and PE Ratio in the Indian Stock Market
Role of PE ratio in investment decisions
In the Indian stock market, PE Ratio plays a significant role in investment decisions. It helps investors gauge the market sentiment and assess the relative valuation of stocks. A high PE Ratio may indicate an overvalued market, while a low PE Ratio may suggest undervaluation.
Market conditions and PE ratio
The PE Ratio of the Indian stock market can vary based on prevailing market conditions, economic factors, and investor sentiment. It is essential to consider these factors when interpreting PE Ratios and making investment decisions.
Foreign investor perspective
Foreign investors often take into account the PE Ratio of a market or specific stocks when making investment decisions. A high PE Ratio may deter long-term foreign investors from investing in a market, while a low PE Ratio may attract value-seeking investors.
10. Case Study: Indian Stock Analysis
Analyzing EPS and PE ratio of Indian companies
To illustrate the practical application of EPS and PE Ratio, let’s consider a case study of analyzing Indian companies. By examining the EPS and PE Ratio of different companies within an industry, investors can identify potential investment opportunities.
Interpreting results and making informed decisions
After analyzing the EPS and PE Ratios of Indian companies, it is crucial to interpret the results in the context of industry trends, company fundamentals, and market conditions. This analysis will enable investors to make informed investment decisions aligned with their investment goals and risk appetite.
11. Tools and Resources for EPS and PE Ratio Analysis
Financial websites and platforms
Several financial websites and platforms provide comprehensive data and tools for analyzing EPS and PE Ratios. These resources offer historical data, peer comparisons, and industry-specific analysis to assist investors in making informed investment decisions.
Analyst reports and recommendations
Analyst reports and recommendations provide valuable insights into a company’s financial performance and future prospects. Analysts often include EPS forecasts, PE Ratio analysis, and investment recommendations, which can be useful for investors seeking expert opinions.
Fundamental analysis techniques
Fundamental analysis techniques, including ratio analysis, are essential for analyzing EPS and PE Ratios. Investors can use fundamental analysis to assess a company’s financial health, profitability, and valuation, providing a solid foundation for investment decisions.
12. Conclusion
Understanding EPS and PE Ratio is crucial for Indian stock investors looking to make informed investment decisions. EPS provides insights into a company’s profitability, growth potential, and industry performance. PE Ratio, on the other hand, helps investors assess a company’s valuation relative to its earnings. By considering these metrics in conjunction with other factors, investors can gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s investment potential and make well-informed decisions.
Investing in the stock market involves careful analysis, continuous learning, and a long-term perspective. By utilizing tools, resources, and fundamental analysis techniques, investors can navigate the complexities of the market and enhance their chances of achieving their investment goals



